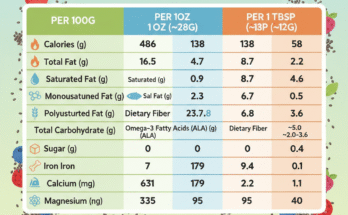
Almonds are one of the most nutrient-dense nuts and are widely recognized for their impressive health benefits. Rich in antioxidants, vitamin E, protein, fiber, and healthy fats, almonds play an important role in supporting heart health, regulating blood sugar levels, and reducing blood pressure.
Scientific research increasingly highlights almonds as a functional food that goes beyond basic nutrition. From antioxidant protection to improved glycemic control, eating almonds regularly may help improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic disease.
This article explores the advantages of eating almonds, backed by research, with a special focus on vitamin E content and blood sugar management.
Nutritional Value of Almonds (Overview)
Before exploring specific advantages, it’s important to understand why almonds are so powerful nutritionally.
Almonds contain:
Vitamin E (one of the richest natural sources)
Plant-based protein
Dietary fiber
Monounsaturated healthy fats
Magnesium, potassium, and calcium
Antioxidant compounds (mainly in the skin)
This combination makes almonds especially beneficial for metabolic health, cardiovascular health, and cellular protection.

1) Almonds Are a Good Source of Vitamin E
One of the most well-documented advantages of eating almonds is their exceptionally high vitamin E content.
Why Vitamin E Matters
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant with several essential roles, including:
Protecting cells from oxidative stress
Reducing inflammation
Supporting immune function
Maintaining healthy skin and blood vessels
Protecting LDL cholesterol from oxidation
Oxidative damage is closely linked to aging, heart disease, and many chronic conditions. Vitamin E helps neutralize free radicals before they damage cells.
Almonds and Vitamin E Content
Almonds are among the best dietary sources of vitamin E worldwide.
Per 1 ounce (28 g):
Vitamin E: 7.27 mg
Equivalent to 48% of the daily value
Few whole foods provide such a high concentration of vitamin E in such a small serving.
Scientific Evidence: Almonds Improve Vitamin E Status
A recent randomized controlled trial examined the effects of almond intake on vitamin E status.
Study Highlights:
Participants: 84 overweight adults
Intervention: 56 g almonds daily
Duration: 4 weeks
Results:
Vitamin E status increased by 102.7%
Carbohydrate-derived energy intake decreased
Improved overall nutrient balance
This study demonstrates that eating almonds daily can significantly improve vitamin E levels, even over a relatively short period.
Why Almond-Based Vitamin E Is More Effective
Vitamin E in almonds is:
Naturally packaged with healthy fats (improves absorption)
Less prone to oxidation compared to supplements
More bioavailable when consumed as whole food
This makes almonds a superior alternative to vitamin E supplementation for many people.

2) May Help Control Blood Sugar Levels
Another major advantage of eating almonds is their impact on blood sugar regulation.
Almonds are:
Low in carbohydrates
High in fiber
Rich in magnesium
Abundant in healthy fats
This nutritional profile supports stable blood glucose levels and improved insulin sensitivity.
Almonds and Glycemic Control
Glycemic control is crucial for:
Preventing insulin resistance
Managing type 2 diabetes
Reducing metabolic syndrome risk
Because almonds have a low glycemic index, they do not cause sharp spikes in blood sugar after eating.
Research Evidence: Almonds Lower Fasting Blood Glucose
24-Week Free-Living Intervention Study
In one study, participants replaced 20% of their daily energy intake with almonds.
Results after 24 weeks:
Lower fasting blood glucose levels
Improved overall glucose stability
This suggests that almonds may positively influence long-term glycemic control when incorporated into daily meals.
Almonds vs Refined Carbohydrates
Unlike refined carbohydrate foods:
Almonds digest slowly
Glucose absorption is gradual
Insulin demand is lower
This is one reason almonds are highly beneficial for individuals at risk of diabetes.

3) Almonds and Type 2 Diabetes Management
Another randomized controlled trial focused on type 2 diabetes patients.
Study Design:
Participants replaced staple carbohydrate foods
Daily intake: 45–55 g almonds
Duration: 12 weeks
Results:
Significant reduction in fasting blood glucose within 3 weeks
Improvements remained after 12 weeks
This shows that substituting almonds for carbohydrates produces measurable blood sugar benefits.
Are Almonds Unique in This Effect?
While other low-carbohydrate foods might show similar effects, this study clearly demonstrated that:
Almonds consistently improved fasting glucose
Benefits were sustained over time
Replacement strategy was effective and practical
The results support almonds as a reliable food choice for glycemic management.

4) Almonds Support Heart Health
One of the best-known almond health benefits is cardiovascular support.
How Almonds Protect the Heart
Lower LDL (bad) cholesterol
Improve HDL (good) cholesterol
Reduce LDL oxidation
Improve blood vessel function
The antioxidants, healthy fats, and magnesium in almonds work together to protect the heart.
Almonds and Blood Pressure Reduction
Almonds may also help reduce blood pressure due to:
Magnesium content (relaxes blood vessels)
Potassium balance
Anti-inflammatory effects
Studies show regular almond consumption supports healthier blood pressure levels, especially in people with metabolic risk factors.

5) Almonds Are Rich in Antioxidants
Most of the antioxidants in almonds are found in the brown skin.
These antioxidants:
Reduce oxidative damage
Protect against inflammation
Work synergistically with vitamin E
Oxidative stress is a major contributor to aging, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer—making antioxidant intake crucial.

6) Helps Support Weight Management
Despite being calorie-dense, almonds are associated with:
Increased satiety
Reduced hunger
Better appetite control
This is because almonds:
Digest slowly
Provide protein + fiber + fat
Reduce cravings for refined carbohydrates
Several studies show almond consumption does not promote weight gain when eaten in moderation.

7) Improves Digestive Health
Fiber in almonds supports gut health by:
Promoting regular bowel movements
Feeding beneficial gut bacteria
Supporting microbiome balance
A healthy gut microbiome is linked to improved immunity, metabolism, and mental health.

8) Benefits of Eating Almonds Daily
Eating almonds daily can:
Improve vitamin E levels
Stabilize blood sugar
Protect heart health
Reduce oxidative stress
Support long-term metabolic health
Recommended Intake
20–30 g per day (about 8–12 almonds)
This amount is supported by research and safe for most individuals.
FAQs
Are almonds healthy to eat every day?
Yes. Moderate daily intake provides consistent antioxidant, heart, and blood sugar benefits.
Do almonds help lower blood sugar?
Yes. Research shows almonds reduce fasting blood glucose, especially when replacing refined carbohydrates.
Are almonds good for people with diabetes?
Yes. Almonds improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic control when eaten in controlled portions.
How much vitamin E do almonds provide?
One ounce provides nearly 48% of the daily vitamin E requirement.
Can almonds reduce inflammation?
Yes. Antioxidants and vitamin E help decrease inflammatory markers.
Conclusion: Why Almonds Deserve a Place in Your Diet
The advantages of eating almonds are supported by strong scientific evidence. Their rich vitamin E content, blood sugar-regulating effects, heart-protective properties, and antioxidant power make almonds one of the healthiest nuts available.
Replacing refined carbohydrates with almonds—even in small amounts—can produce meaningful improvements in metabolic health, blood sugar levels, and nutrient intake.
When eaten regularly and in moderation, almonds are not just a snack—but a functional food that supports long-term health.