Chia Seeds for Brain Health: Boost Memory, Focus & Mood Naturally
Brain health is central to productivity, mood, and long-term mental resilience. Chia seeds — tiny but nutrient-packed — supply plant-based omega-3s, fiber, antioxidants, and minerals that support brain function. In this evidence-informed guide we’ll cover how chia contributes to memory, focus, and mood, the science behind it, practical serving tips, recipes, and how to combine chia with other brain-boosting foods.
Quick links: For the full context, see our pillar article 10 Proven Health Benefits of Chia Seeds, practical prep guide How to Eat Chia Seeds for Maximum Benefits, and seed comparison Chia Seeds vs Flax Seeds. Try the interactive Chia Seed Nutrition Calculator for custom servings.
Why nutrition matters for the brain
Your brain needs a steady supply of nutrients to form neurotransmitters, maintain cell membranes, and regulate inflammation. Diets rich in omega-3s, antioxidants, B-vitamins, and minerals (magnesium, zinc) are associated with better cognitive performance and lower risk of age-related decline. Chia seeds contribute to several of these categories — making them a valuable component of a brain-supportive diet.
What in chia seeds supports brain health?
Let’s break down the key nutrients in chia that matter for cognition and mood:
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) — a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid that supports neuronal membrane fluidity and anti-inflammatory processes. While ALA conversion to EPA/DHA is limited, regular ALA intake still correlates with better cardiovascular and cognitive outcomes compared with low-omega diets.
- Antioxidants — polyphenols and flavonoids in chia reduce oxidative stress, which damages brain cells over time.
- Fiber — slows glucose absorption, stabilizes blood sugar, and supports gut health (linked to the gut-brain axis).
- Minerals — calcium, magnesium, manganese — all important cofactors for neurotransmitter synthesis and neuronal function.
Nutrition snapshot — typical values per 2 tablespoons (≈28 g)
| Nutrient (per 2 tbsp / 28 g) | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | ≈137 kcal |
| Protein | ≈4.4 g |
| Fiber | ≈10.6 g |
| Omega-3 (ALA) | ≈4.9–5.0 g |
| Calcium | ≈177 mg |
| Magnesium | ≈95 mg |
| Antioxidant index (proxy) | Moderate–High |
Values are approximate (USDA & nutrition databases). Use our nutrition calculator for customized servings.
How chia supports memory & focus — mechanisms that matter
1. Cell membrane integrity & neuronal signaling
Omega-3 fatty acids are integral components of neuronal cell membranes. ALA contributes to the pool of omega-3s in the body that influence membrane fluidity, neurotransmitter receptor function, and synaptic signaling — all fundamental for memory and attention.
2. Reducing neuroinflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to cognitive decline. Chia’s omega-3s and polyphenols help lower inflammatory markers; less inflammation can mean better neural function and resilience.
3. Blood sugar stability for better concentration
Large glucose swings impair attention and mood. Chia’s soluble fiber slows carbohydrate absorption and helps maintain steady blood glucose, supporting sustained focus during the day.
4. Gut-brain axis — fiber and mental health
Fiber-rich foods like chia feed beneficial gut bacteria. The microbiome produces short-chain fatty acids and neurotransmitter precursors (like tryptophan metabolites) that influence mood and cognition via the gut-brain axis.
What the research says — a short review
Direct randomized trials of chia specifically for cognition are limited. However, broader evidence for omega-3s (especially EPA/DHA) supports cognitive benefits. Because ALA conversion to EPA/DHA is limited, combining chia with other sources (fish, algae supplements) or ensuring consistent dietary ALA can be part of a brain-healthy pattern. Observational studies link plant-based omega-3 intake with better cognitive outcomes compared with low-omega diets.
Note: If your primary goal is maximizing EPA/DHA (for specific clinical needs), consider discussing algae-based DHA/EPA supplements with a clinician. Chia is excellent for overall nutrition and long-term brain support, especially for plant-based diets.
Daily serving suggestions for brain support
- General maintenance: 1 tablespoon (≈10–15 g) daily mixed into meals or smoothies.
- Enhanced support: 2 tablespoons (≈28 g) daily — chia pudding, smoothie, or mixed in yogurt.
- Combine with other omega-3 foods: walnuts, hemp seeds, and fatty fish (if you eat fish) for better omega-3 diversity.
7 brain-boosting ways to add chia to meals
- Morning chia pudding with berries & walnuts — berries for antioxidants, walnuts for plant omega-3s.
- Chia & Greek yogurt bowl — protein + fiber for neurotransmitter precursors and satiety.
- Chia + smoothie with spinach & banana — potassium and B-vitamins for neural function.
- Chia-crusted salmon — if you eat fish, combines plant and marine omega-3s.
- Chia in oatmeal with cinnamon — cinnamon supports insulin sensitivity; oats provide steady energy.
- Chia-laced salad dressings — drizzle chia-based dressing to get micro-doses throughout the day.
- Chia nut butter spread — blend chia into nut butter for a brain-nourishing toast.
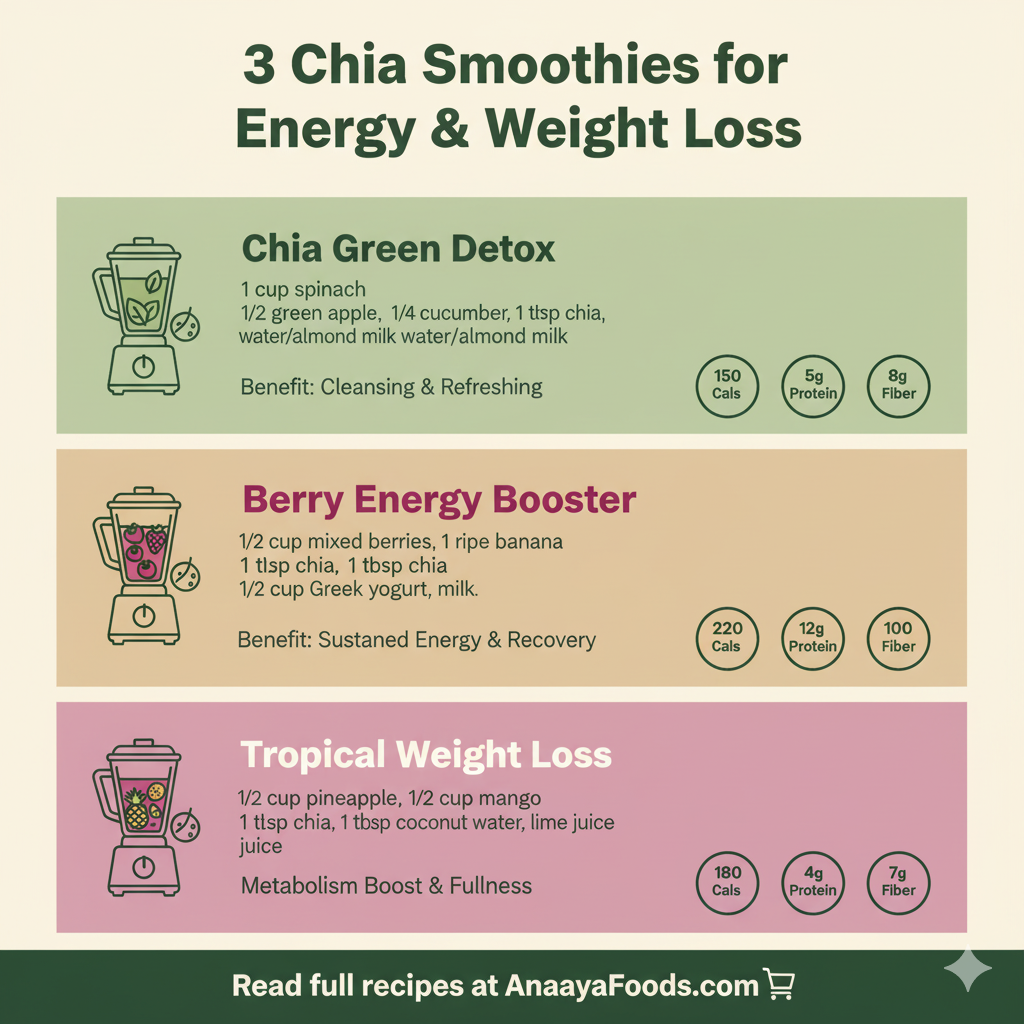
Quick brain-boosting recipe: Berry Chia Memory Smoothie
1 cup unsweetened almond milk, 1/2 cup mixed berries, 1 tbsp chia (soaked 5–10 min), 1 tbsp walnuts (or 1 tsp walnut butter), 1/2 banana, 1 scoop protein powder (optional). Blend until smooth.
Food pairing & synergy — maximize benefits
Pair chia with foods that supply complementary nutrients for cognition:
- Vitamin B sources: eggs, legumes, quinoa — B-vitamins help form neurotransmitters.
- Antioxidant partners: blueberries, dark leafy greens, green tea.
- Magnesium sources: almonds, pumpkin seeds, dark chocolate (in moderation).
Practical tips for consistency and absorption
- Hydrate chia: soaking improves texture and digestion for larger portions.
- Rotate seeds: use flax and hemp alongside chia for a fuller nutrient profile.
- Store properly: keep chia in a cool, dark place; refrigerate after opening for long shelf life.
Affiliate picks — brain-friendly pantry & gear (sample Amazon links)
Below are sample Amazon search links you can replace with your affiliate URLs.
Shop organic chia seeds on Amazon
Shop walnuts on Amazon
Shop blenders on Amazon
How long until you see brain-related changes?
Some cognitive effects (improved focus, steadier energy) may be noticeable within days due to blood sugar stabilization and reduced energy crashes. Long-term benefits like improved memory, mood stability, or neuroprotection require consistent dietary patterns over months and are influenced by genetics, sleep, exercise, and overall diet quality.
Who should be cautious?
- Medication interactions: If you take blood-thinning drugs, consult your doctor when increasing omega-3 intake.
- Digestive sensitivity: increase fiber gradually to avoid bloating.
- Allergies: rare, but discontinue if allergic reactions occur.
Infographic prompt — Pinterest & designer ready

Internal links & further reading
- 10 Proven Health Benefits of Chia Seeds
- How to Eat Chia Seeds for Maximum Benefits
- Chia Seed Smoothie Recipes for Energy & Weight Loss
- Chia Seeds vs Flax Seeds
FAQ
Can chia seeds improve memory?
Chia supports memory indirectly by supplying omega-3 ALA, antioxidants, and stabilizing blood sugar. While direct clinical trials on chia and memory are limited, the nutrient profile supports cognitive health as part of a balanced diet.
Are chia seeds good for mood?
Yes — by supporting gut health, reducing inflammation, and providing steady energy, chia can help mood stability. Other lifestyle factors (sleep, exercise) are also key.
How should kids eat chia for brain development?
Small servings (1 tsp–1 tbsp) in yogurt or smoothies are appropriate for most children. Consult a pediatrician for infants or specific health concerns.